The Dead Sea Scrolls: 11 Fascinating Facts

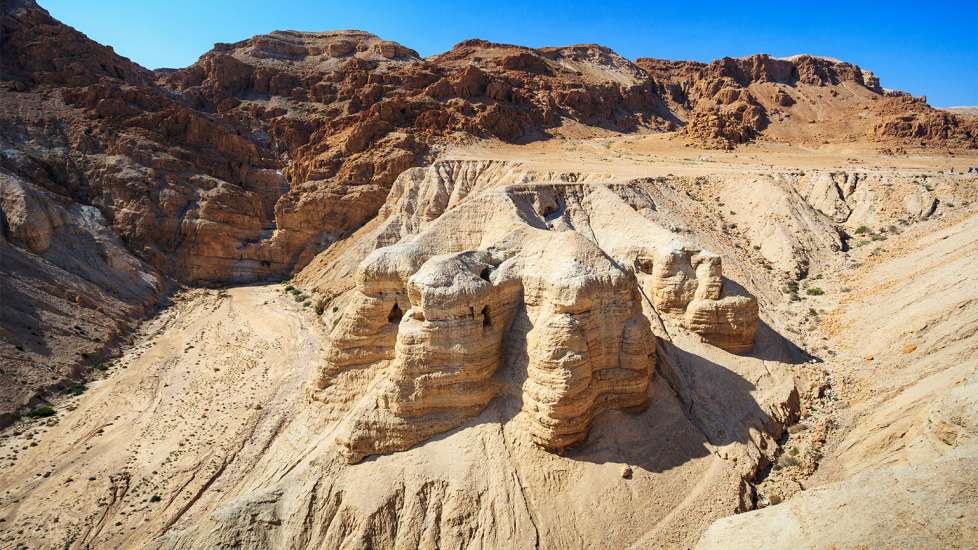
The Dead Sea Scrolls are one of the most startling discoveries of the 21st century. In 1947, a Bedouin shepherd boy stumbled upon something remarkable while herding his goats off the northwest shore of the Dead Sea in Israel, an area known as Qumran. Click through below to discover some incredible facts about one of the greatest archaeological finds of all time, one that continues to shape our understanding of the Bible today.

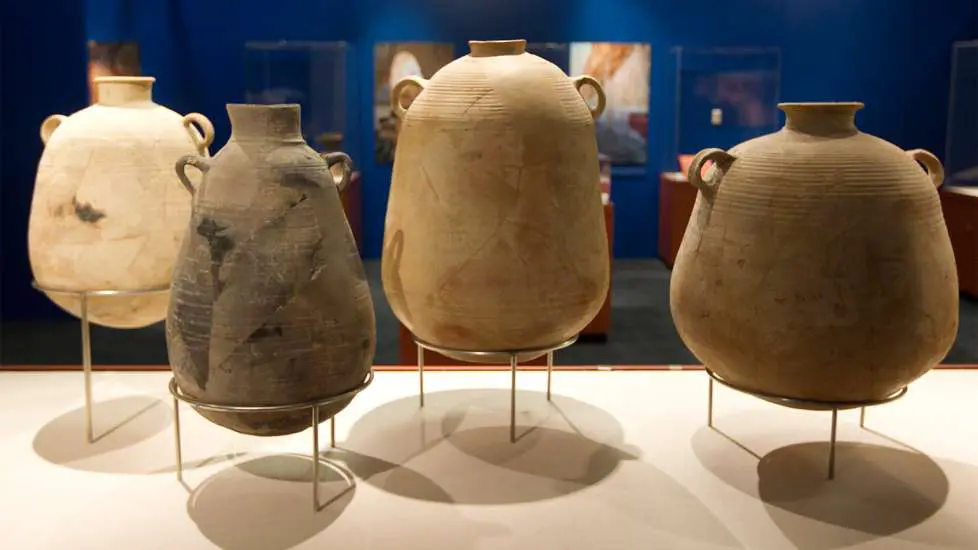
1. The Bedouin shepherd, who belonged to the Ta’amireh tribe, had been looking for a lost goat when he came across the cave in Qumran. He assumed his goat had gotten stuck inside. So he tossed a rock in the cave’s narrow opening to see if the goat would respond. To his surprise, the sound of pottery shattering echoed out instead. He returned days later with others in his tribe and found tall, clay jars inside the cave.

1. The Bedouin shepherd, who belonged to the Ta’amireh tribe, had been looking for a lost goat when he came across the cave in Qumran. He assumed his goat had gotten stuck inside. So he tossed a rock in the cave’s narrow opening to see if the goat would respond. To his surprise, the sound of pottery shattering echoed out instead. He returned days later with others in his tribe and found tall, clay jars inside the cave.

2.Many of the jars were empty. However, some contained scrolls that were carefully wrapped in linen that had blackened over time. The shepherds removed seven scrolls and eventually handed four of them over to an antiquities dealer in Bethlehem named Kando.
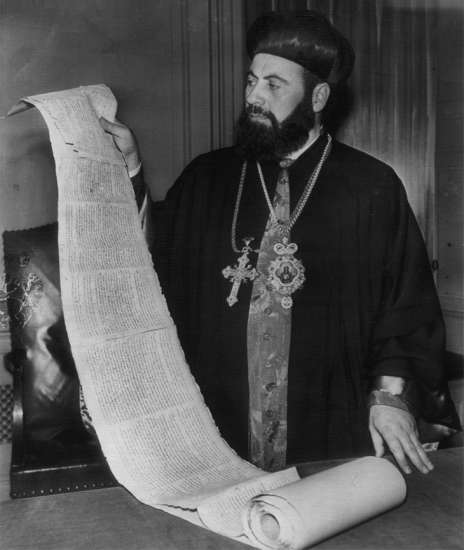

3.Kando assumed the scrolls were written in Aramaic and brought them to the attention of Athanasius Yeshue Samuel, an Aramaic-speaking archbishop at St. Mark’s Monastery in Old Jerusalem. Unfortunately, Archbishop Samuel couldn’t read the text since the scrolls were written in Hebrew. But he couldn’t deny there was something about them. He purchased four scrolls from Kando for about $100.

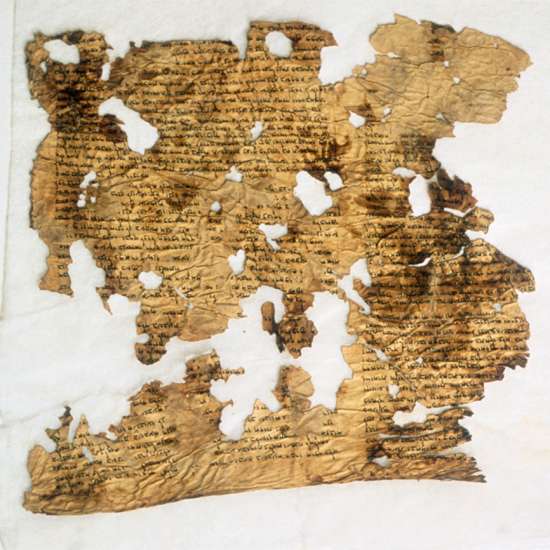
4. Eventually, the scrolls in Archbishop Samuel’s possession were authenticated as books of the Bible dating as far back as 150 B.C. One of the scrolls was in fact the Book of Isaiah, which was 1,000 years older than any previously known copy of the manuscript. It was also the most complete scroll found—with only a few minor damages—and was 24 feet long.
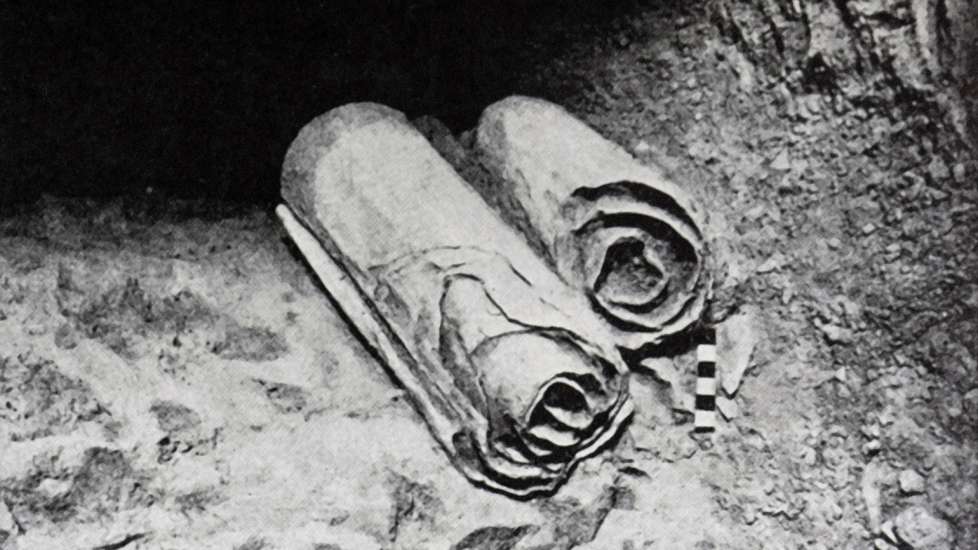

5. Since 1947, thousands more scroll fragments have been discovered in the 11 caves of Qumran, with more than 900 manuscripts found in total. The scrolls include an almost complete collection of the Hebrew Bible, as well as religious texts that shed light on life in the years before Jesus’ birth. The only book of the Old Testament never found was the Book of Esther. Some believe it dissolved over time or is still waiting to be discovered in Qumran.

6. Most of the Dead Sea Scrolls were written in Hebrew, with several in Aramaic and Greek. One of the most fascinating scrolls uncovered was made out of copper—the only scroll not made from animal skin or parchment. It was found in the third cave of Qumran and contained a treasure map leading to buried gold, silver and copper.

7. Many scholars believe the scrolls are mostly likely the work of the ancient Essenes, a Jewish sect that occupied Qumran in the first centuries B.C. and A.D. According to historians, they referred to themselves as the “Sons of Light” and devoted their lives to penning and preserving sacred texts.
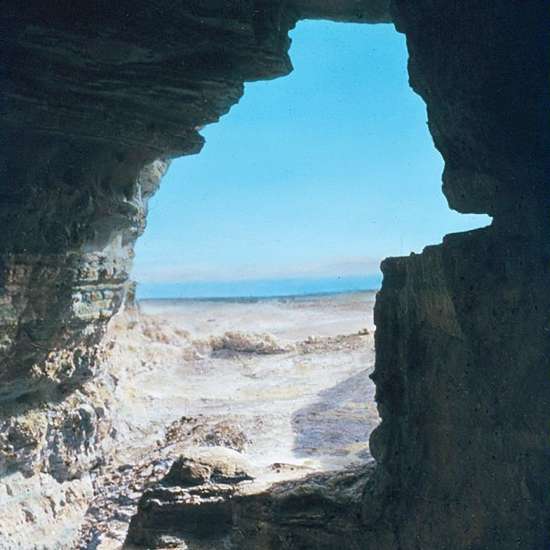

8. So why did the Essenes hide the scrolls in the caves of Qumran? One theory suggests they did so to protect their work from the “Sons of Darkness,” aka the Roman army. Sensing an impending attack, they hid their scrolls in the one place the Romans would never think to look. In 68 A.D., the Roman army wiped out the Essene community and the scrolls remained hidden for nearly 2,000 years.

9. The discovery of the Dead Sea Scrolls has proved to be of great importance to the scholarly community, helping researchers better understand the link between Judaism and Christianity. The scrolls also contained previously unknown stories about Biblical figures like Enoch, Abraham and Noah.
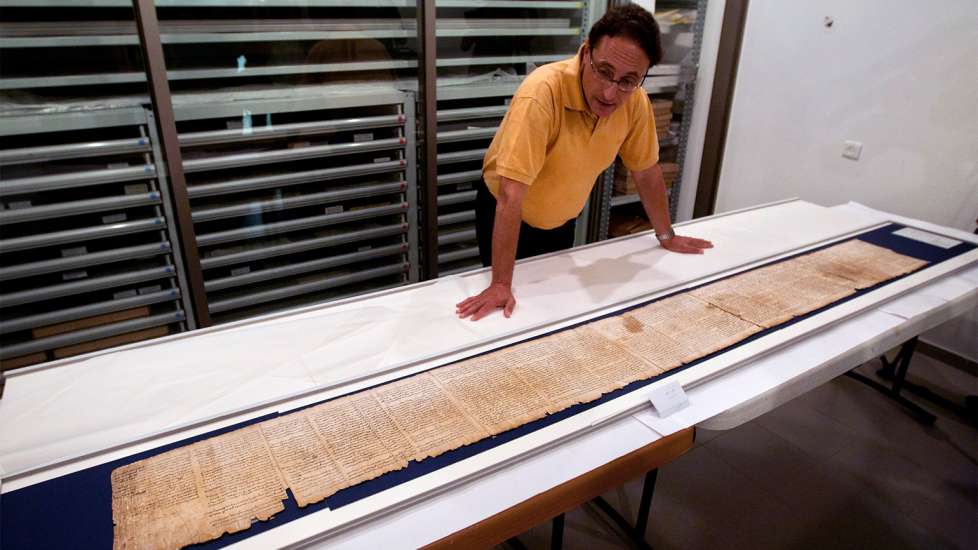

10. Today, the scrolls are housed in two locations in the Holy Land: the Rockefeller Museum and the Israel Museum. Over time, experts have figured out how to copy the cave conditions in Qumran, where the scrolls survived for so many years, in order to better preserve the ancient manuscripts.
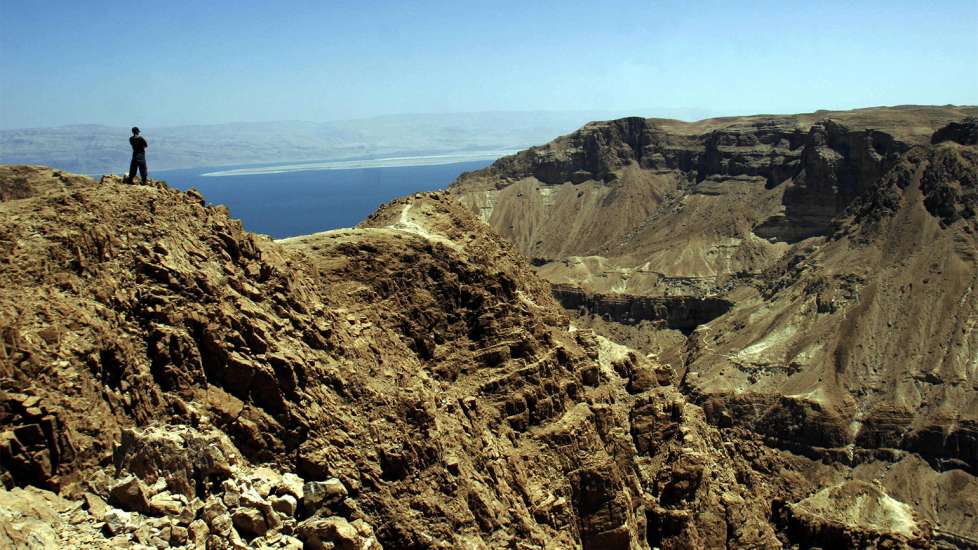

11. The story of the Dead Sea Scrolls isn’t over yet. Recently, archaeologists found a 12th cave in Qumran that contained broken scroll jars. And, according to CNN, there are still hundreds more caves in the Dead Sea region left to explore.
Editor’s Note: For more on this on other important news, please learn more at the Guideposts Magazine website.
Recommended Posts
The Lord’s Words
April 20, 2018

An Unlikely Path to Success
April 20, 2018

Miraculously Reunited with the Aydin Cross
April 20, 2018

